In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has evolved from a niche technology to a transformative force reshaping multiple industries. Among its most exciting applications is generative AI, particularly in the realm of image creation, including AI-generated portraits and headshots. This blog post will show you the intricacies of the rise of generative AI, exploring its technological foundations, artistic implications, and ethical considerations, while also examining its broader societal impacts.
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI refers to algorithms that can generate new content based on existing data. At the core of this technology is a class of models known as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). Developed by Ian Goodfellow and his team in 2014, GANs consist of two neural networks—the generator and the discriminator.
- The Generator: This network creates images from random noise, aiming to produce output indistinguishable from real images.
- The Discriminator: This network evaluates the images, determining whether they are real or generated.
Through this adversarial process, both networks improve over time, leading to the production of highly realistic images.
The Technical Breakdown
Generative AI leverages vast datasets – such as thousands of photographs of human faces – to learn the underlying patterns and features that define a “real” image. The result is a capability to synthesize new images that exhibit the nuances of human expression, texture, and color. Recent advancements have extended beyond GANs to models like diffusion models, which generate images by gradually transforming random noise into coherent pictures. This approach has shown promising results in terms of image quality and fidelity.
Transforming Portrait Creation
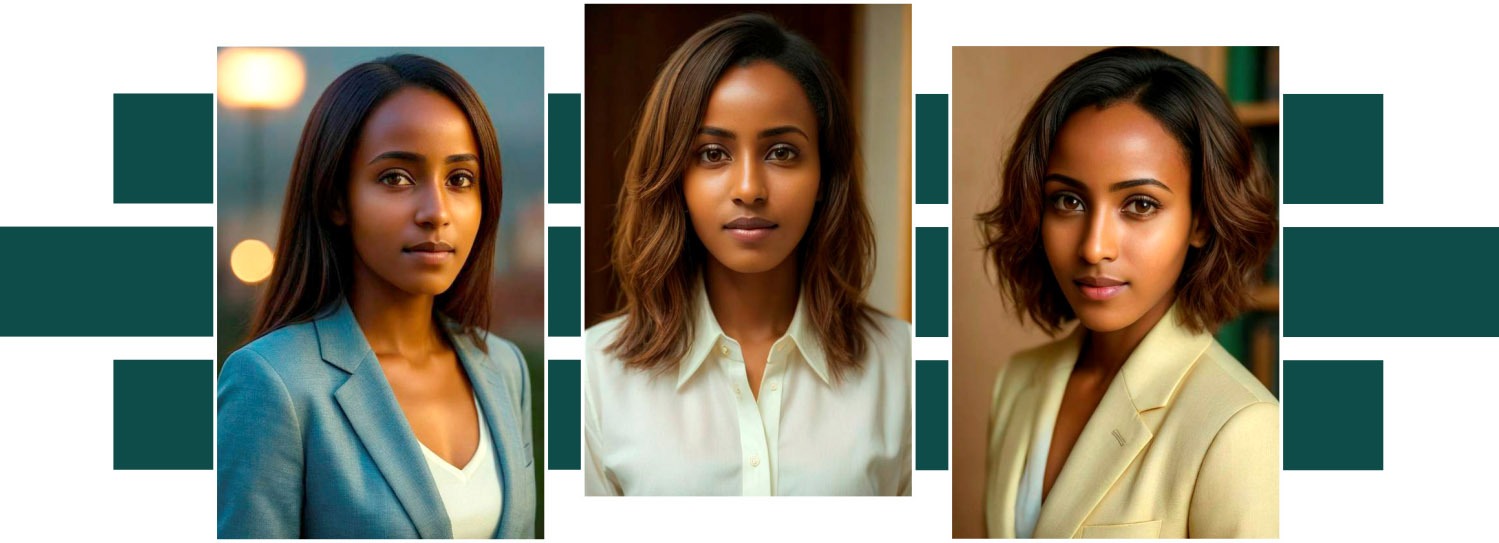
AI-generated portraits are revolutionizing traditional artistic practices. No longer confined to the brushstrokes of human artists, the creation of portraits can now be executed by algorithms that analyze and synthesize countless elements. This democratizes art production, allowing individuals without formal artistic training to create visually striking portraits.
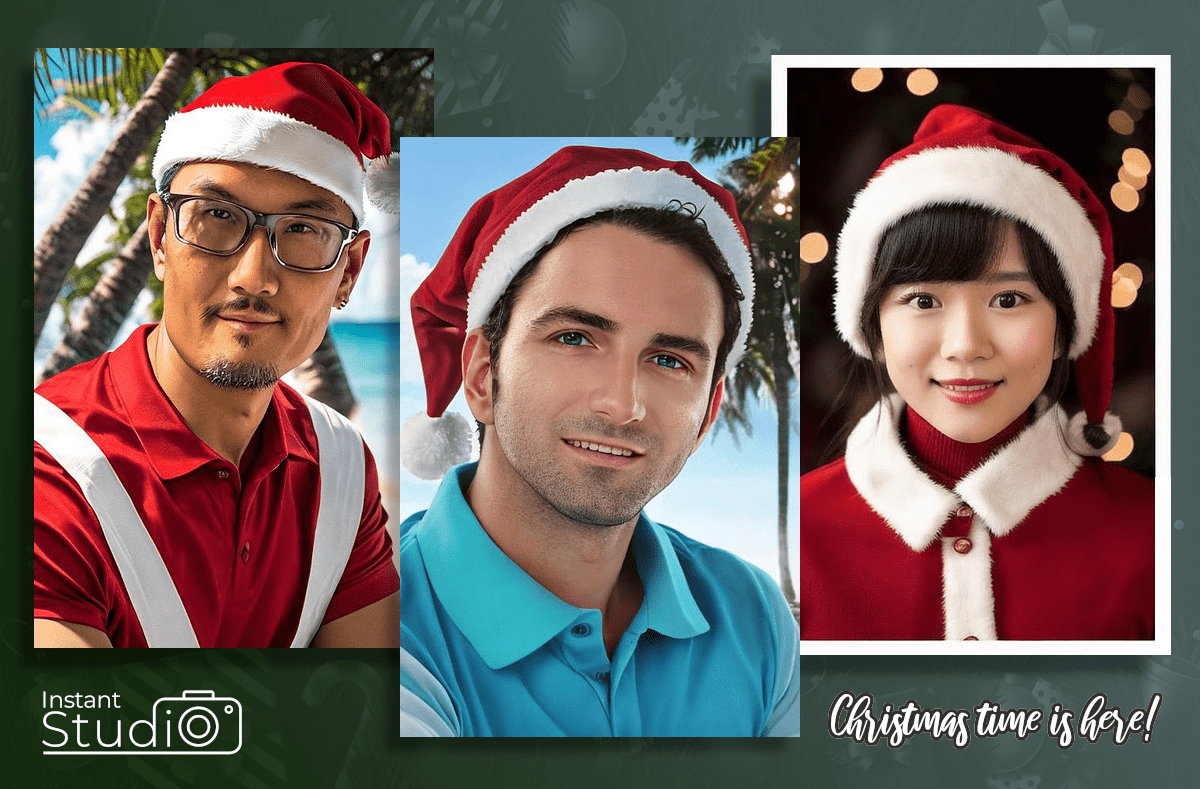
Platforms like InstantStudio Toolkit and other AI generating programs enable users to input textual prompts, resulting in unique images generated from the description provided. This melding of language and visuals signifies a new frontier for artistic expression.
Applications in Personal Branding
In a digital age where personal branding is essential, AI-generated headshots are gaining traction. Businesses and professionals are utilizing these portraits for social media, websites, and marketing materials. The ability to create high-quality images quickly and affordably allows brands to maintain a polished and consistent online presence.
Healthcare
AI’s impact extends far beyond art. In healthcare, generative AI is being used for various applications, such as creating detailed medical images for diagnostic purposes. By analyzing patient data, AI can generate tailored treatment plans, predict disease progression, and even assist in surgical procedures, enhancing both accuracy and efficiency.
Entertainment
In the entertainment industry, AI is transforming the way content is created. From generating scripts to composing music and producing visual effects, AI tools are streamlining production processes. AI-generated characters in films and video games create richer narratives and immersive experiences, allowing creators to push the boundaries of storytelling.
Education
AI’s capabilities also extend into education, where personalized learning experiences are becoming more common. AI-driven platforms can assess a student’s learning style and performance, generating tailored resources that cater to individual needs. This adaptability enhances the learning process, making education more accessible and engaging.
Marketing and Advertising
In marketing, AI algorithms analyze consumer behavior and preferences, allowing companies to craft personalized campaigns that resonate with target audiences. Generative AI can create eye-catching visuals and copy that attract consumers, ultimately driving sales and engagement.
The Ethical Landscape
While the advancements in generative AI are exciting, they also raise important ethical questions. Here are some considerations:
Copyright and Ownership
The issue of copyright in AI-generated art is a complex and evolving topic. If an AI model generates a portrait based on the styles of famous artists, who owns the rights to that image? The original artists? The developers of the AI? The users who prompted the creation? As legislation struggles to keep pace with technology, these questions remain largely unanswered.
Misuse and Deepfakes
The ability to generate realistic images raises concerns about misuse, particularly in the context of deepfakes – hyper-realistic, AI-generated videos or images that can be used to mislead or manipulate. This technology can create false narratives, perpetuate disinformation, and damage reputations. Addressing these concerns requires robust ethical guidelines and regulations.
Representation and Bias
AI models are trained on existing datasets, which can carry inherent biases. For instance, if a model is trained predominantly on images of certain demographics, it may not accurately represent others. This could lead to the reinforcement of stereotypes or the erasure of marginalized identities in AI-generated content. Developers must prioritize diverse datasets and ethical AI practices to mitigate these risks.
The Future of AI and Portraiture
The future of generative AI in portraiture is bright and filled with possibilities. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated AI models capable of producing lifelike images with unprecedented detail. Here are some potential future trends:
AI in Fashion:
Generative AI can also influence fashion design, creating unique clothing patterns and styles based on current trends, further blurring the lines between art and technology.
Hyper-Personalization:
Future AI systems may enable users to create highly personalized portraits, incorporating individual traits, styles, and preferences with greater nuance.
Collaboration Between Humans and AI:
Artists may increasingly collaborate with AI tools to enhance their creative processes, blending human intuition with computational power to produce innovative artworks.
Virtual Reality Integration:
As virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies advance, AI-generated portraits may find new applications in immersive environments, allowing users to interact with AI-created personas in real-time.
The key take-away
The Rise of Generative AI is not merely a technological marvel; it is a catalyst for change in the world of art and personal branding. As we navigate the opportunities and challenges presented by AI-generated images, it’s crucial to embrace innovation while addressing the ethical implications that arise. The intersection of AI and art promises to reshape our understanding of creativity, identity, and representation, paving the way for a future where human and machine collaboration thrives.
In this exciting era, we must remain vigilant, thoughtful, and creative, ensuring that the evolution of AI in portraiture serves to enrich our lives and broaden our artistic horizons. As we look ahead, the canvas of generative AI remains blank, inviting us to explore the limitless potential it holds.